摘要
- volatile线程工作副本的可见性
- synchronized:关键步骤加锁
线程的创建
继承Thread
public class Thread1 extends Thread{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void main(String[] a)
{
new Thread1().start();
}
}
实现Runable
public class Thread2 implements Runnable{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void main(String[] a)
{
new Thread(new Thread2()).start();
}
}

图片alt

图片alt

图片alt

图片alt
java多线程信息共享
通过共享变量在多个线程中共享消息
- static变量
- 同一个Runnable类的成员变量
public class ThreadDemo0
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
new TestThread0().start();
new TestThread0().start();
new TestThread0().start();
new TestThread0().start();
}
}
class TestThread0 extends Thread
{
//private int tickets=100; //每个线程卖100张,没有共享
private static int tickets=100; //static变量是共享的,所有的线程共享
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
if(tickets>0)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" is selling ticket " + tickets);
tickets = tickets - 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
TestThread1 t=new TestThread1();
new Thread(t).start();
new Thread(t).start();
new Thread(t).start();
new Thread(t).start();
}
}
class TestThread1 implements Runnable
{
private int tickets=100;
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
if(tickets>0)
{
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
tickets--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" is selling ticket " + tickets);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
}
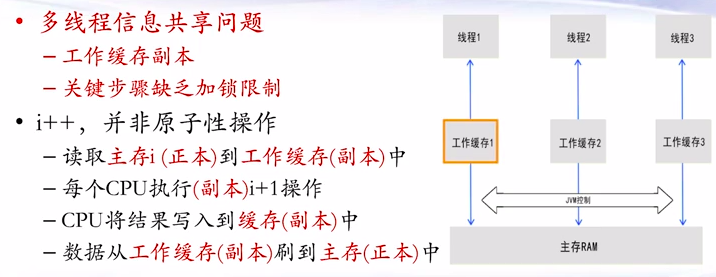
图片alt

图片alt
volatile 让所有线程及时看到变量值的变化
public class ThreadDemo2
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
TestThread2 t = new TestThread2();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
t.flag = false;
System.out.println("main thread is exiting");
}
}
class TestThread2 extends Thread
{
// boolean flag = true; //子线程不会停止
volatile boolean flag = true; //用volatile修饰的变量可以及时在各线程里面通知
public void run()
{
int i=0;
while(flag) // t.flag = false; 工作缓存的flag是true 需要加入volatile
{
i++;
}
System.out.println("test thread3 is exiting");
}
}

图片alt
public class ThreadDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread3 t = new TestThread3();
new Thread(t, "Thread-0").start();
new Thread(t, "Thread-1").start();
new Thread(t, "Thread-2").start();
new Thread(t, "Thread-3").start();
}
}
class TestThread3 implements Runnable {
private volatile int tickets = 100; // 多个 线程在共享的
String str = new String("");
public void run() {
while (true) {
sale();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
if (tickets <= 0) {
break;
}
}
}
public synchronized void sale() { // 同步函数
if (tickets > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is saling ticket " + tickets--);
}
}
}
参考
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/35878d4ec130
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39747568/article/details/112872830
问题
- tomcat在配置时设置最大线程数,当前线程数超过这个数值时会出错,那么有没有办法捕获到这个错误,从而在client端显示出错信息?