模板存在的意义
求两个整数、浮点数、字符的最大值?
C语言实现
int maxInt(int x,int y);
double maxDouble(double x, double y);
char maxChar(char x,char y);
C++函数重载
函数名称相同
int maxValue(const int& x,const int& y);
double maxValue(const double& x, const double& y);
char maxValue(const char& x,const char& y);
int maxValue(const int& x,const int& y){
if(x>y)return x;
return y;
}
double maxValue(const double& x, const double& y){
if(x>y)return x;
return y;
}
char maxValue(const char& x,const char& y){
if(x>y)return x;
return y;
}
函数模板
#include <iostream>
template <typename T, typename S>
auto add (T x1, S x2) { //C++14
return (x1 + x2);
}
int main () {
auto y = add ( 1, 2.0 );
std::cout<<y<<std::endl; //3
return 0;
}
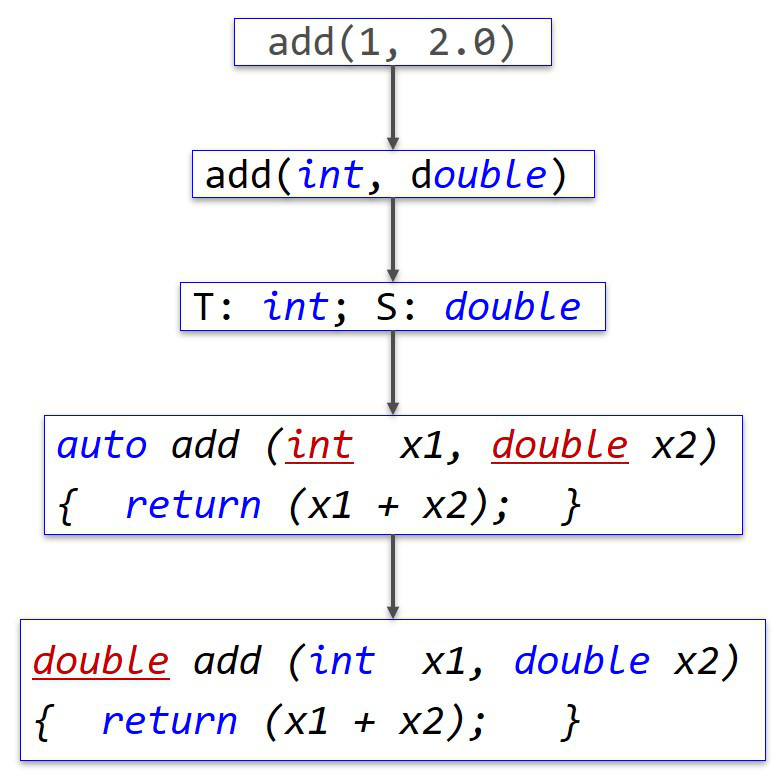
图片alt
函数模板实例化
显式实例化
template < typename T >
void f( T s ){
std::cout << s << '\n';
}
template void f<double>(double);
template void f<>(char); // 实例化 f<char>(char) ,推导出模板实参
template void f(int); // 实例化 f<int>(int) ,推导出模板实参
// 实例化,编译器生成代码
// void f(double s) { // T: double
// std::cout << s << '\n';
// }
隐式实例化
#include <iostream>
template<typename T>
void f(T s) {
std::cout << s << '\n';
}
int main(){
f<double>(1); // 实例化并调用 f<double>(double)
f<>('a'); // 实例化并调用 f<char>(char)
f(7); // 实例化并调用 f<int>(int)
void (*ptr)(std::string) = f; // 实例化 f<string>(string)
}
typedef和using在定义别名时的区别
template <typename T>
typedef std::vector<T> v;//使用typedef
template <typename T>
using v = std::vector<T>;//使用using
使用typedef时,编译器会报错error: template declaration of ‘typedef’
C++编译器不支持使用typedef关键词为模板类设置别名,但是使用using的方式声明一个关键词却是允许的。只是这个是C++11标准才有的,如果在编译时不加上--std=c++11使用新的标准的话,编译器一样会报错。
#include <iostream>
namespace space //隔离模板,避免冲突
{
template<class T> using ptr = T*;//模板的简写
}
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
typedef int(*ADD)(int a, int b);
using FUNC = int (*)(int a, int b);//别名
//int(*p)(int a,int b)为函数指针,去掉p视为类型。
using co = std::ios_base::fmtflags;//using只可以用于简写数据类型
void main()
{
ADD p=add;
std::cout<<p(1, 2)<<std::endl;
FUNC func = add;
std::cout << func(1, 2) << std::endl;
space::ptr<int> pint(new int(15));//创建一个类型为int的指针 并采用括号()方式对其初始化
std::cout << *pint << " " << pint << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}